
The members of the research group are:
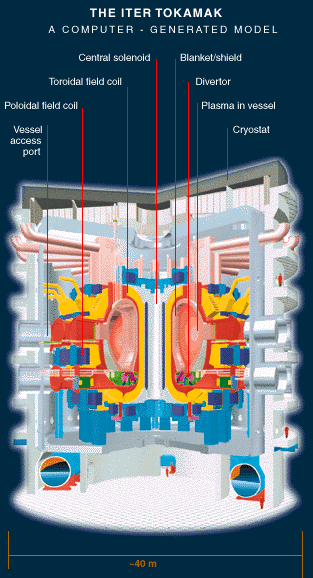
ITER is an international consortium aimed at the design of an experimental fusion reactor based on the "tokamak"
concept in which the plasma is created and confined in a toroidal chamber by an appropriately shaped magnetic field. The size of the machine and the objectives
persecuted make ITER the largest project in the field of Nuclear Fusion research.
The activity of the group concerns the problem of controlling the current, shape and position of the plasma inside the chamber.
In tokamaks, there are two components of the confining magnetic field. A set of toroidal field coils, evenly spaced around the torus provides a strong toroidal magnetic field that is kept constant during the whole discharge and provides for plasma stability. The second component, the poloidal field, is responsible for the equilibrium of the plasma. It is produced by the plasma current and can be shaped by using the set of Poloidal Field Coils. The current is induced in the plasma by transformer action, where the primary is constituted by the full set of Central Solenoid and Poloidal Field Coils and the secondary is the plasma ring.
The activity of the Padova group, carried on in close collaboration with the Poloidal field and Plasma Control Division of the ITER Joint Central Team (Naka, Japan), focuses on the problem of control and optimisation of the poloidal field configuration that determines plasma current, position and shape.
The main phases involved in the design of a Control System, from plant modelling to the design of controllers, are considered. In particular, research has been performed on the following topics: